Significance
In continuum mechanics, an energy cascade involves the transfer of energy from large scales of motion to the small scales. Inverse energy cascade in three-dimensional isotropic turbulence. Currently, numerous applications have been based on the inverse energy flux phenomena. Ideally, inverse energy flux can be observed when an azimuthally polarized beam with vortical phase is sharply focused with a high numerical aperture lens. In the past, it has been shown that inverse energy flux could be obtained by the sharp focusing of higher order radially polarized laser beams. Furthermore, the integrated inverse energy flow increases with increase in the topological order of incident radially polarized laser beams. Hence, it is relevant to generate cylindrical vector beams of higher orders. Presently, there are a few methods for the creation of cylindrical vector beams where each of the available approaches has its pros and cons. Consequently, there is need to develop a novel approach that circumvents the various challenges experienced in the available techniques.
In a recent publication, Russian scientists at Samara National Research University from the Department of Technical Cybernetics and IPSI RAS – Branch of the FSRC “Crystallography and Photonics” RAS: Dr. Sergey Degtyarev, Dr. Dmitry Savelyev, Professor Svetlana Khonina and Professor Nikolay Kazanskiy, developed a novel approach to construct meta-surfaces for the generation of inverse energy flux near the optical axis. Specifically, in contrast to sectorial subwavelength gratings, they applied the continuous shape of ridges that provide a more homogeneous transformed polarization. Their work is currently published in the research journal, Optics Express.
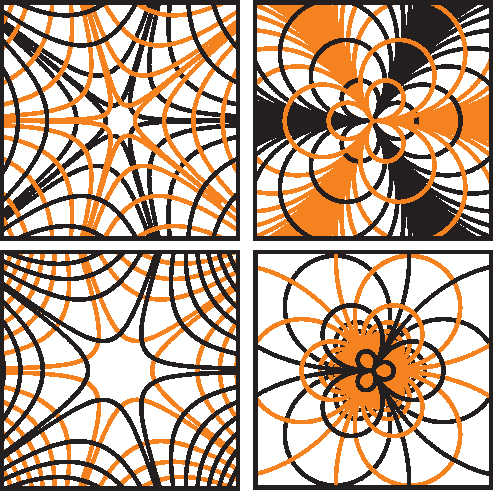
The research team derived novel equations intended to create continuous subwavelength relief for transformation of a linearly polarized input field into a radially polarized beam with an arbitrary order. In other words, for them to create continuous subwavelength relief, they had to derive new phase functions equations. All in all, the curves of the slow and fast axes of the proposed photonic-crystal subwavelength gratings were plotted.
The authors observed that by combining the two functions of polarization and phase transformations in one element, they were able to decrease the number of elements in an arrangement. In addition, results from the numerical simulations demonstrated the formation of the inverse energy flux in the focal region. Further, the integrated inverse energy flux that was achieved with the third order meta-surface was 2.8 times higher than the integrated inverse energy flux achieved with the second-order meta-surface.
In summary, the study demonstrated successfully a family of optical elements for the formation of an inverse energy flux in a focal region. Technically, the aforementioned elements take the form of subwavelength gratings with curved ridges. Remarkably, new expressions were obtained for the phase functions of the polarizing subwavelength gratings, which convert a linearly polarized beam into a radially polarized beam of arbitrary order. Overall, in an interview with Advances in Engineering, Dr. Dmitry Savelyev highlighted that the usefulness of the element was the continuous relief that provides more efficient polarization transformation especially in adjacent thin annular zones of high numerical aperture focusing phase. Polarization transformation control allows creating light fields with new properties for using laser beams that can change the nature of the impact on the object. It is very important in tasks such as laser cutting and engraving in processing materials.

Reference
Sergey Degtyarev, Dmitry Savelyev, Svetlana Khonina, Nikolay Kazanskiy. Metasurfaces with continuous ridges for inverse energy flux generation. Volume 27, Number 11 | 2019 | Optics Express 15129
Go To Optics Express Advances in Engineering Advances in Engineering features breaking research judged by Advances in Engineering advisory team to be of key importance in the Engineering field. Papers are selected from over 10,000 published each week from most peer reviewed journals.
Advances in Engineering Advances in Engineering features breaking research judged by Advances in Engineering advisory team to be of key importance in the Engineering field. Papers are selected from over 10,000 published each week from most peer reviewed journals.