Significance
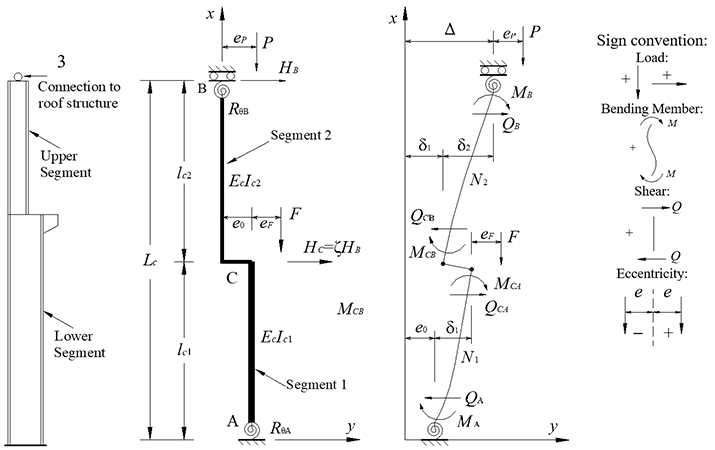
The frames used in mill buildings need to be robust enough to withstand the high crane loads. Usually, such frames are made of stepped columns with a lighter upper segment and a heavy wide-flange cross-section lower segment to accommodate the crane load. However, unlike prismatic columns, stepped columns exhibit considerably varying buckling behavior due to the effects of the non-uniform cross-section and the presence of axial (crane) load. To this end, the buckling behavior of stepped columns has drawn significant research attention. Since Timoshenko’s pioneering works in the 1970s, numerous theoretical and experimental studies have been carried out to calculate the buckling loads of different columns, establish their effective length factors and mechanical behaviors. These studies have satisfactorily addressed various problems associated with buckling behaviors and have been extended to multi-step and non-uniform columns. Following the previous studies, design protocols for stepped columns have been established and adopted.
Despite the progress, most existing studies concentrate on the behaviors of individual columns while neglecting the effects of the interaction amongst different columns, leading to inaccurate frame design. In an effort to address this challenge, a couple of hand manual hand-design methods have been developed to determine the effective length factors as well as buckling loads used in the design of stepped columns. Unfortunately, the existing methods are not suitable for some design scenarios, such as pitched-roof portal frames and multi-bay frames, since they ignore the inclination angles of the roof and interaction effects amongst columns. Therefore, developing a design method applicable to all design scenarios is highly desirable.
Although computer software and finite element modeling are quite popular, hand calculation methods are indispensable because they better comprehend the design process and mechanical behaviors of the columns. Therefore, Dr. Weifeng Tian, Professor Jiping Hao, Professor Weihui Zhong from Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology proposed a simple and accurate hand calculation method for evaluating the second-order effects and effective length factors on stepped column-based frames. This method accounts for the interaction effects amongst different stepped columns. The work is currently published in the Journal of Construction Steel Research.
The proposed method was based on the concept of negative stiffness that is applicable to different frame types. This concept was used to calculate effective length factors accounting for the interaction effects amongst different stepped columns. Next, the second-order effects were theoretically analyzed to develop expressions to determine the moment amplification and deflection factors. The authors also presented a practical method considering the influence of roof angles with stepped columns. Lastly, the practicability of the proposed method was validated through nonlinear static and eigenvalue analysis.
Results demonstrated the superiority of the proposed method in capturing the interaction effects of different columns and providing accurate estimates of effective length factors than the existing methods. A satisfactory estimation of the second-order effects with 0.6% and 3.4% differences in displacement and bending moment, respectively, was achieved. The slight inaccuracy of the bending moment was attributed to the simplification of the column deformation curve. In addition, the proposed method accurately accounted for the influence of roof angle, and it applies to a wide range of frame types
In summary, a simple and feasible approach for calculating effective length factors and evaluating the buckling behavior of stepped columns by considering the interaction effects of multiple columns were reported. The method enabled the authors to use stiffness factor values corresponding to lateral load coefficient to ensure the physical significance of the expressions and equations used to calculate the effective length factors. The results demonstrated the validity and practicability of the proposed approach. The authors further provided recommendations for improving the current design codes. In a statement to Advances in Engineering, authors said their study findings and the recommendations will enable engineers and fabricators to develop cost-effective and reliable designs for stepped columns in mill buildings.


Reference
Tian, W., Hao, J., & Zhong, W. (2021). Buckling of stepped columns considering the interaction effect among columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 177, 106416.
 Advances in Engineering Advances in Engineering features breaking research judged by Advances in Engineering advisory team to be of key importance in the Engineering field. Papers are selected from over 10,000 published each week from most peer reviewed journals.
Advances in Engineering Advances in Engineering features breaking research judged by Advances in Engineering advisory team to be of key importance in the Engineering field. Papers are selected from over 10,000 published each week from most peer reviewed journals.



